Disclaimer: This article is translated with the assistance of AI.
What is Ectopic Pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy, also known as eccyesis or ectopic gestation, occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. Over 90% of cases happen in the fallopian tubes, but it can also occur in the cervix, ovaries, or even the abdomen. In such situations, the fertilized egg usually can’t survive, and the pregnancy must be terminated promptly to avoid life-threatening risks to the mother.
Ectopic Pregnancy Incidence Rates
According to the 2014 annual report from the Hong Kong College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, ectopic pregnancy accounted for 3.7% of all pregnancy complications. Compared to 2009 data, the incidence rate rose by 28.6% in 2014. Additionally, the rates for ectopic pregnancies in different locations are as follows:
| Location of Ectopic Pregnancy | Incidence Rate |
| Fallopian Tube | 98% |
| Ovary | 1.7% |
| Caesarean Scar | 0.17% |
| Abdomen | 0.17% |
| Cervix | 0% |
- * This data is from a 2014 study by the Hong Kong College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, with a total of 594 participants
Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms & Signs
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy typically appear between the 4th and 12th weeks of pregnancy. Since early pregnancy often shows no signs, it’s usually discovered during routine prenatal check-ups or when more severe symptoms emerge later.
These symptoms can mimic common gastrointestinal issues, so they’re easy to overlook. If untreated, the misplaced embryo may grow and cause the fallopian tube to rupture or lead to heavy bleeding—prompt treatment, possibly including tube removal, is crucial.
| Common Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms | Less Common (More Severe) Symptoms |
|
|
What Causes Ectopic Pregnancy? How to Prevent It?
Medical research has yet to pinpoint the exact cause of ectopic pregnancy, and there’s no foolproof way to prevent it entirely. Since the main culprit is often inflammation of the fallopian tubes from sexually transmitted infections, we recommend practicing safe sex—think fewer partners and proper condom use—to lower the risk of tubal inflammation or other STIs. Plus, if you’re a smoker, kicking the habit ASAP can help reduce your chances. Once pregnancy is confirmed, get those prenatal check-ups early to safeguard you and your baby. If you notice vaginal bleeding or unexplained dull pain or bloating in your lower abdomen during pregnancy, stay alert and see a doctor right away for a proper diagnosis.
Ectopic Pregnancy High-Risk Groups
While the exact cause of ectopic pregnancy remains unclear in medical research, it’s commonly linked to narrowing or blockage of the fallopian tubes. Certain individuals face a higher risk, including those with:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease: Inflammation of the female reproductive organs, often spread through sexual contact
- A history of ectopic pregnancy: These women have about a 10% chance of recurrence
- Previous tubal ligation surgery
- History of in vitro fertilization: Medications that aid ovulation can increase the risk
- Accidental pregnancy while using an intrauterine device (though rare)
- Smoking
- Advanced maternal age (women aged 35 to 40)
There’s no surefire prevention for ectopic pregnancy yet, but using condoms correctly to avoid STIs and quitting smoking can effectively lower the risk.
How to Diagnose Ectopic Pregnancy? How Soon?
If your pregnancy test is positive but you’re experiencing ectopic pregnancy symptoms, seek medical help promptly for an ultrasound scan . If no gestational sac is visible, it could be ectopic, requiring further diagnosis to prevent serious or even life-threatening complications.
Doctors can’t diagnose ectopic pregnancy through a clinical pelvic exam alone, as it only assesses things like ovarian or tubal tumors. Diagnosis typically involves transvaginal ultrasound and blood tests.
- Transvaginal ultrasound is an invasive procedure where a small probe is inserted into the vagina. It uses reflected sound waves to get precise images of the uterus and ovaries up close. It’s quick, doesn’t require anesthesia, and allows the doctor to immediately check if the embryo has implanted in the wrong spot.
- If the ultrasound doesn’t confirm ectopic pregnancy, the doctor may draw blood to test for human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels, usually repeating it two or more times, 48 hours apart, to monitor changes. In ectopic cases, hCG levels are typically lower and rise more slowly, helping to spot the difference. This also aids in choosing the best treatment. Results usually take a few hours to a day.
Can a Pregnancy Test Detect Ectopic Pregnancy?
A pregnancy test can only confirm pregnancy initially—it can’t detect if it’s ectopic.
Ectopic Pregnancy Impacts and Complications
If the embryo implants incorrectly in the fallopian tube and continues to develop there, it can cause the limited space in the tube to rupture, leading to severe consequences like massive bleeding, miscarriage, or even death. As for the detached embryonic tissue, if the placental function remains intact, it might re-implant in another abdominal location, developing into an abdominal pregnancy.
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment and Surgery Options
A fertilized egg cannot develop outside the uterus, so the ectopic pregnancy tissue and any affected fallopian tube or ovarian tissue must be removed to prevent serious or even fatal complications from residual embryonic tissue. During surgery, doctors will preserve reproductive organs as per the patient’s request to maintain fertility.
Treatment options for ectopic pregnancy include medication, conservative surgery, or radical surgical removal:
- Medication Treatment
Early ectopic pregnancies without significant bleeding can be treated with medication like methotrexate, which stops cell growth and breaks down existing cells to halt the ectopic pregnancy. Methotrexate is administered via intramuscular injection, and doctors will monitor blood levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to ensure the dosage is adequate and effective.
- Conservative Surgical Removal
Salpingostomy is a conservative procedure where the doctor makes an incision in the fallopian tube to remove the fetal tissue, allowing the tube to heal itself. The downside is that it may not completely remove all fetal tissue.
- Radical Surgical Removal
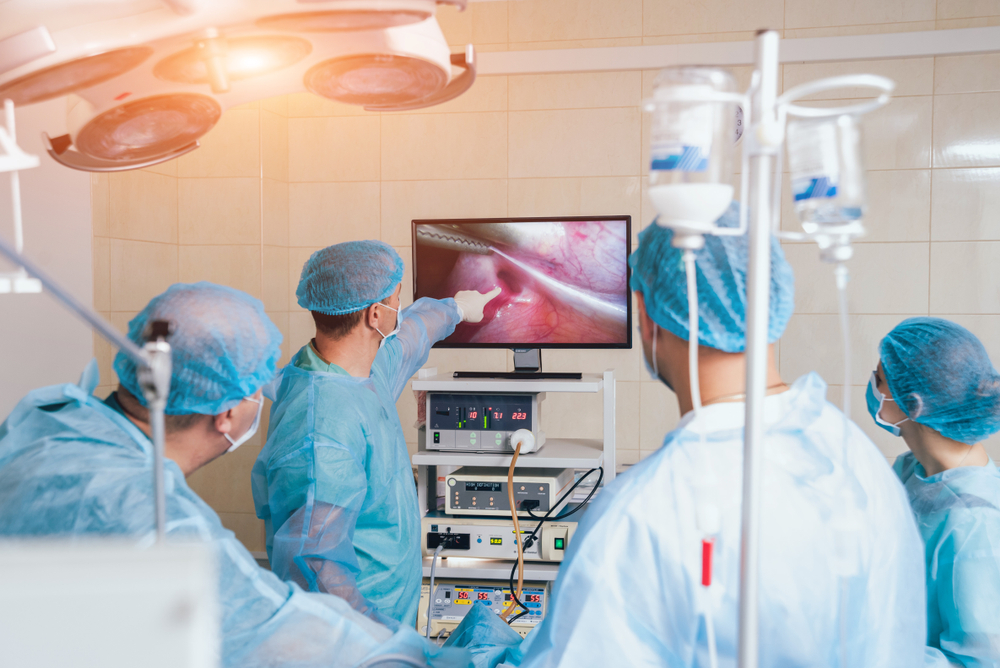
Salpingectomy involves completely removing the fetal tissue along with the entire affected fallopian tube, while preserving the other healthy tube. Both procedures are laparoscopic ectopic pregnancy surgeries, where the doctor makes small incisions in the abdomen and uses a laparoscope to perform the operation.
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment Cost Guide
Assuming an ectopic pregnancy patient undergoes minimally invasive surgery and stays in a general ward, the cost is approximately HK$70,000 to HK$90,000.
Women who have experienced an ectopic pregnancy, even after a salpingectomy, can still get pregnant again with proper treatment. It’s recommended to wait at least 3 months after medication treatment before trying to conceive, to avoid any negative effects on the fetus. Overall, about 65% of women successfully conceive again within 18 months after an ectopic pregnancy, with only a few needing in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Women with a history of ectopic pregnancy have a higher chance of recurrence compared to those without, with a recurrence rate of about 10%.