Disclaimer: This article is translated with the assistance of AI.
What is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a common childhood illness that occurs mostly in children under 5 2 , caused by enteroviruses such as Coxsackievirus and Enterovirus 71 1 . According to the World Health Organization , in most cases, HFMD is a self-limiting and mild viral infection, with dehydration being the most common complication 4 .
The Hong Kong Red Cross educational leaflet points out that HFMD draws attention due to its highly contagious nature 6 . A medical article from Mayo Clinic shows that there is still no targeted treatment for HFMD; frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals are the most effective ways to reduce infection risk in children 3 .
According to Union Hospital and the Department of Health website , HFMD patients are most contagious in the first 7 days of illness, and fecal transmission can last for several weeks 8 . The virus is mostly spread through the following routes 1 :
- Contact with patients’ nasal or throat secretions, saliva, and feces
- Contact with patients’ ruptured blisters
- Touching contaminated objects like toys, utensils, towels, floor mats, etc.
After infection, the virus typically incubates in the body for about 3 to 6 days 3 .
Hand Foot Mouth Disease Peak Season in HK
According to the Centre for Health Protection’s data , in Hong Kong, May to July is the peak season for hand, foot, and mouth disease, with a smaller peak from October to December 1 .
Hand Foot Mouth Disease Symptoms & Early Signs
The early symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease are relatively mild, including 7 :
- Mild fever : Body temperature may rise to 37.5°C to 38.5°C.
- Sore throat : Children may complain of throat discomfort or difficulty swallowing.
- Small red spots in the mouth : Small red spots appear in the mouth, which may later develop into blisters or ulcers.
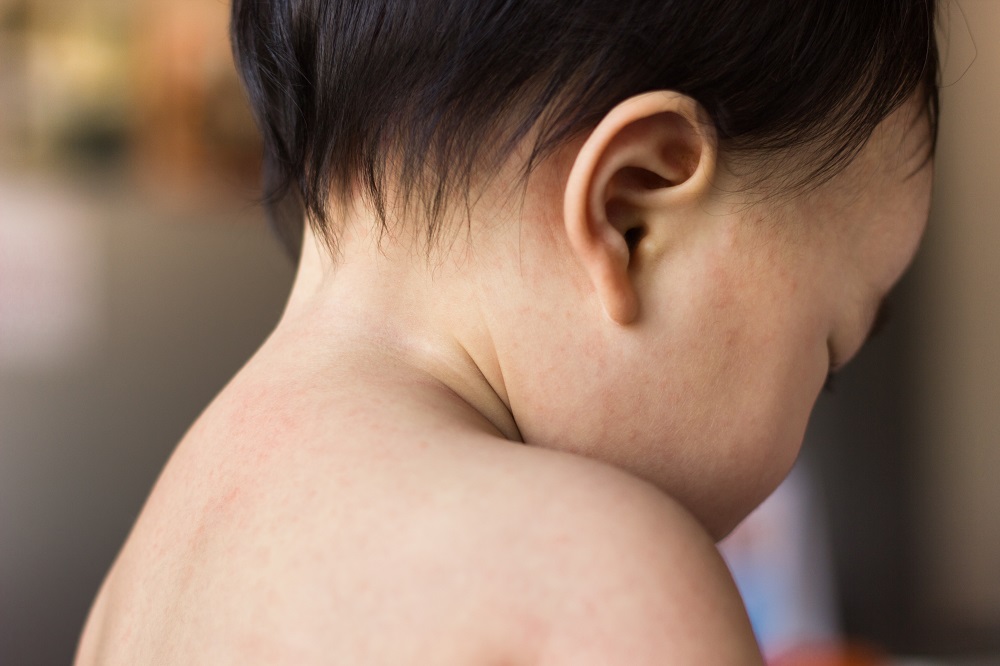
- Red spots on hands, feet, and sensitive areas : Small red spots start appearing on palms, soles, genitals, or buttocks, gradually forming blisters.
3 to 6 days after infection, patients will exhibit the following symptoms 2,4,5 :
- Fever : Elevated body temperature is a typical symptom of hand, foot, and mouth disease, usually lasting 1 to 2 days.
- Mouth ulcers : Small blisters or ulcers appear in the mouth (such as on the tongue or gums), causing pain and difficulty eating.
- Rashes on palms and soles : Red spots or blisters appear on palms, soles, or buttocks; these rashes are usually not itchy.
- Sore throat : Due to mouth ulcers, patients may feel throat discomfort.
- Loss of appetite : Mouth pain leads to children being unwilling to eat.
- Headache : Some patients may feel tired or have headaches.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease caused by enterovirus 71 may lead to the following severe complications 1 :
- Viral meningitis
- Encephalitis
- Polio-like paralysis
In the most severe cases, it can lead to death.
If you’re worried your child has hand-foot-and-mouth disease , parents should closely monitor their condition. If symptoms worsen, such as persistent high fever , repeated vomiting, drowsiness, limb weakness, or a dazed expression, seek medical attention immediately 1 .
- * Full reimbursement means no sub-limit on compensation and applies only to specified benefit items. Payable claims are subject to the remaining deductible (if applicable), annual benefit limit, lifetime benefit limit, and other conditions including reasonable and customary charges, pre-existing conditions, designated hospital list in Mainland China, and treatments in the US. For detailed product terms and conditions, product risks, and exclusions, please refer to the relevant product website and policy.
Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease Treatment
Mayo Clinic medical article states that there’s currently no medication to treat hand-foot-and-mouth disease; only drugs to relieve fever and pain from mouth ulcers 3 . Most patients with mild symptoms recover on their own within 7 to 10 days . Since dehydration is the most common complication, patients should drink plenty of water and rest 1 .
Additionally, OT&P Healthcare article notes that patients with hand-foot-and-mouth disease may have difficulty swallowing due to rashes and ulcers, so it’s recommended to consume cool and liquid foods, such as:
- Ice cream
- Yogurt
- Jelly
- Tofu pudding
Avoid eating overly hot, spicy, or acidic foods that could irritate the ulcer wounds and affect healing, such as congee water and fruit juice.
Due to its high contagiousness, avoid going to school, participating in group activities, or visiting crowded places until fully recovered (i.e., fever and rashes subside, and all blisters scab over) to prevent spreading the virus to others. If the infection is caused by Enterovirus 71, patients should stay home for an additional 2 weeks after full recovery before returning to school 9 .
Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease Prevention Tips
As mentioned above, the virus spreads through bodily secretions. The CDC recommends that the best way to prevent it is by maintaining good personal and environmental hygiene 4 :
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after changing diapers, using the toilet, coughing, sneezing, or blowing your nose.
- Help children wash their hands and keep blisters clean.
- Avoid touching your face with unwashed hands, especially your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces and shared items, including toys and door handles.
- Avoid close contact with infected people, such as hugging or kissing them.
Since hand, foot, and mouth disease is caused by different enteroviruses, even after recovery, you could still get infected by other enteroviruses causing HFMD . So, it doesn’t mean you’ll have lifelong immunity after one bout. That’s why maintaining personal and environmental hygiene is key to avoiding infection 1 !
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease FAQs
Adults can get infected too ! Unlike children, adults with HFMD might only show rashes or mouth ulcers, or even have no symptoms at all. 10
According to the Centre for Health Protection website , many people develop antibodies to the specific enterovirus after recovering from HFMD.
However, since multiple enteroviruses can cause HFMD, you could still get it again from a different one 1 .
- 1 Centre for Health Protection. Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease. 6 July 2023, www.chp.gov.hk/tc/healthtopics/content/24/23.html.
- 2 Department of Health. Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease. 21 May 1999, www.dh.gov.hk/tc_chi/press/1999/21_05_99.html.
- 3 Mayo Clinic. Hand-Foot-And-Mouth Disease. 16 Aug. 2022, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hand-foot-and-mouth-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20353035.
- 4 CDC. About Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease. 7 May 2024, www.cdc.gov/hand-foot-mouth/about/index.html.
- 5 World Health Organization. Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease. www.who.int/westernpacific/emergencies/surveillance/archives/hand-foot-and-mouth-disease.
- 6 Hong Kong Red Cross. Beware of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease. 9 Oct. 2018, www.redcross.org.hk/sites/redcross/files/media/hcs_files/Health%20Express/HE-201810-v2_0.pdf.
- 7 Trinity Medical Centre. Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease. trinitymedical.com.hk/en/hand-foot-mouth-disease/.
- 8 Union Hospital. HFMD is Contagious: Remember Personal Hygiene. www.union.org/new/tc_chi/health_info/health_articles_child4.htm.
- 9 OT&P Healthcare. Symptoms, Prevention and Risk of HFMD in Adults. www.otandp.com/en-hk/health-information/hand-foot-and-mouth-disease.
- 10 Hong Kong Red Cross. Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease. 28 Aug. 2019, www.redcross.org.hk/sites/redcross/files/media/hcs_files/Health%20Express/HE-201908.pdf.