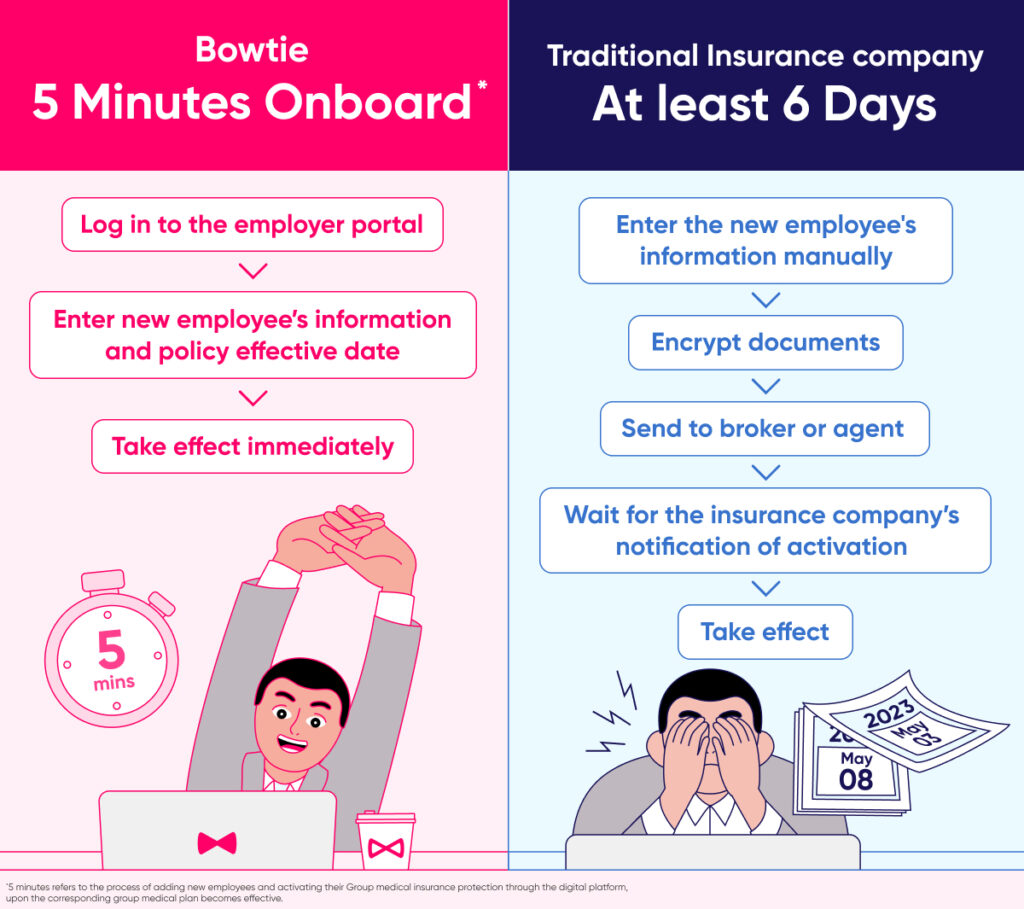
What is laparoscopy? What are its main applications in gynecology?
Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery, involves the use of a flexible endoscope tube with a light source and camera to enter the abdominal or pelvic cavity through one or more small incisions made in the patient’s abdomen. This procedure is divided into diagnostic and therapeutic types, allowing for proper diagnosis and treatment of various conditions.
Due to the ability of doctors to perform detailed examinations of the pelvic or abdominal organs through laparoscopy, it is widely used in gynecology in addition to its common applications in gastroenterology and urology. It enables more accurate diagnosis, identification of causes, and treatment of gynecological diseases such as ovarian cysts and endometriosis.
Laparoscopy has two primary applications
Diagnostic Examination
The doctor makes a small incision in the patient’s abdomen and inserts a tube with a light source and camera to directly examine organs such as the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. It is primarily used to investigate the causes of abdominal or pelvic pain, tissue tumors, diagnose endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease, check for tubal blockages, and identify the causes of infertility.
Surgical Treatment
Through laparoscopic surgery, doctors can perform various procedures, including:
- Removal of inflamed appendix (appendectomy)
- Removal of the gallbladder to treat gallbladder inflammation caused by gallstones (cholecystectomy)
- Partial removal of the intestine to treat conditions like ineffective medication in Crohn’s disease or diverticulitis (colectomy)
- Hernia repair or removal to cure hernias
- Repair of ruptured or bleeding gastric ulcers
- Gastric bypass or gastric sleeve surgery to treat obesity
- Removal of organs affected by malignant tumors, such as the uterus, prostate, liver, intestines, kidneys, or bladder
- Treatment of ectopic pregnancies to remove the embryo and prevent damage to the fallopian tubes
- Removal of fibroids
- Hysterectomy for the treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, excessive menstrual flow, or pain.
Laparoscopic/Minimally Invasive Examination and Surgical Fees
| Private Hospital / Medical Center | Fees |
| Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital |
|
| St. Paul’s Hospital |
|
| Hong Kong Adventist Hospital – Stubbs Road |
|
| Gleneagles Hospital Hong Kong |
|
| Canossa Hospital |
|
| Matilda & War Memorial Hospital |
|
| Saint Teresa’s Hospital |
|
| Hong Kong Baptist Hospital |
|
| Evangel Hospital |
|
| Precious Blood Hospital (Caritas) |
|
| Hong Kong Adventist Hospital – Tsuen Wan |
|
| Union Hospital |
|
| CUHK Medical Centre |
|
| Hospital Authority |
|
- NoteThe above data was obtained from official websites on January 16, 2022. The prices listed are the 50th percentile total charges for regular wards and are provided for reference purposes only.
Laparoscopy/Minimally Invasive Examination and Surgery Insurance Notes
Most laparoscopic surgeries are covered by voluntary health medical scheme. Bowtie’s voluntary health medical scheme fexi Plan allows customers to choose their coverage and only requires a monthly fee of $200 (uniform charge for all ages). By purchasing Bowtie’s Gleneagles Hospital Medical and Health Combo, designated surgeries or examinations can be fully compensated*. Some of the laparoscopic procedures covered include:
- Laparoscopic-assisted total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy ($126,700)
- Laparoscopic myomectomy ($107,700)
- Laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy ($85,100)
- Laparoscopic ectopic pregnancy removal ($88,500)
- Diagnostic laparoscopy +/- tubal patency test ($40,500)
- Laparoscopic bilateral tubal ligation ($48,300)
- *Full compensation refers to the coverage limit of the voluntary medical insurance Flexi Plan policy year.
- ^The above prices are the total package prices provided by Gleneagles Hospital for reference. The Bowtie Medical Information Team collected this information on January 18, 2021, from the official website.
Examination/Surgery Procedure and Steps
Most laparoscopic procedures are performed under general anesthesia. During the surgery, the patient is positioned with the head down and feet up to allow gravity to move the organs away from the pelvis, facilitating the laparoscopic procedure.
The surgeon will make one or two small incisions on the patient’s abdominal skin. The first incision (approximately 1 to 1.5 cm) is made below the navel, and through this incision, the surgeon will insert a cannula to introduce carbon dioxide into the abdominal cavity. This is mainly done to create space inside the abdominal cavity, allowing the surgeon to have a clear view of the internal organs and facilitating disease diagnosis or surgical treatment.
The second incision is usually used to insert the laparoscope, which is equipped with a light source and a camera. The location of this incision depends on the position of the organ being examined. Once the laparoscope is inserted, the surgeon directly examines the intended area using the images transmitted through the laparoscope or displayed on a TV monitor.
If a surgical treatment is required, the surgeon will make additional small incisions on the skin to insert the necessary surgical instruments. For example, in the case of appendix removal, the surgeon may need to make a third small incision in the abdomen to guide the instruments for the removal procedure, guided by the images from the laparoscope.
After the completion of the entire laparoscopic procedure, the surgeon will remove all instruments, release the carbon dioxide gas from the abdomen through the laparoscope, and then suture all incisions, applying appropriate dressings.
Pre-Examination/Surgery Preparation
- During the menstrual cycle, appropriate contraceptive measures should be taken to ensure that the surgery is performed without pregnancy.
- Before admission, patients should bathe at home with disinfectant soap and thoroughly clean the surgical site (abdomen).
- Since one of the incisions is near the navel, it is recommended to clean the navel with a cotton swab soaked in soap the day before the surgery.
- After the surgery, there may be a small amount of vaginal bleeding, and the patient should bring a sufficient number of sanitary pads to the hospital.
- Patients should bring loose clothing to the hospital for easy changing when discharged to avoid touching the wound and causing pain.
- If the surgery is arranged as a day surgery, an adult should be arranged to accompany the discharge at an appropriate time.
- You should not eat or drink at least 6 hours before the surgery.
- Before the surgery, personal clothing or jewelry should be removed and replaced with a surgical gown provided by the hospital.
- If the patient has nail polish, it should be wiped off before admission.
- Patients need to stop taking blood thinners or anticoagulants a few days before the surgery as directed by the doctor.
Examination/Surgery Risks and side effects
Laparoscopic examination or surgery is a lower risk medical procedure, but there may be potential side effects:
- Infection and inflammation of the abdominal wound
- Bleeding or bruising of the skin near the abdominal wound
- Nausea or dizziness caused by anesthesia
- Damage to nearby blood vessels, intestines, or urinary organs
- As laparoscopic surgery requires the injection of carbon dioxide to expand the abdomen, too much carbon dioxide can stimulate the diaphragm, causing pain in both shoulders, and there is also a chance that air may enter the arteries/veins causing subcutaneous emphysema after the operation.
- Severe allergic reaction to anesthesia
- As more complex laparoscopic surgeries take longer, patients may accumulate blood clots in their leg veins due to lying down for a long period of time, which can lead to severe deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism.
FAQ
- Drink plenty of fluids and eat more fruits and vegetables to avoid straining the abdomen due to constipation, which may affect the healing of wounds in the abdominal cavity.
- If necessary, take painkillers as prescribed by your doctor. After surgery, you may feel dizzy or nauseous because the effects of the anesthetic have not completely dissipated.
- You can first eat lighter foods such as soup and porridge that are easier to digest.
- You should avoid eating more irritating foods after the operation.
- During the surgery, carbon dioxide will be injected into the abdominal incision, so pain in the shoulder or ribs is a normal sequelae. If the pain is unbearable, you can ask the medical staff for painkillers.
- After laparoscopic surgery, the wound is very small and the pain is lower, so patients are often encouraged to get out of bed and move around as soon as possible to avoid pneumonia caused by long-term bed rest.
Doctors usually cover the postoperative wound with waterproof dressings. It is recommended to pay attention to whether there is bleeding or excessive exudation on the dressing, and to go to the hospital regularly after discharge for the doctor to examine the wound. - After the operation, you should avoid vigorous exercise or lifting heavy objects to avoid overuse of the abdominal muscles.
- When coughing or sneezing, you should press to fix the abdominal wound to reduce the pain caused by vibration.
- If the following situations occur, you should seek medical attention immediately: fever, severe lower abdominal pain, red, swollen, hot and painful wounds, abnormal secretions or odors.