Disclaimer: This article is translated with the assistance of AI.
What is Hives? Types of Hives
Hives ( urticaria) , also known as wind rash, is a common sudden allergic skin condition that’s not contagious. It can be divided into chronic and acute hives. Affected skin shows red patches of varying sizes that are extremely itchy. The onset of hives is hard to predict, and symptoms usually fade within 24 hours.
| Chronic Hives | Acute Hives |
| Symptoms of chronic hives often recur for 6 weeks or more, linked to immune system imbalances. Treatment might take months or even years. | Symptoms of acute hives usually heal within a few weeks, with traceable causes often from external triggers. Since onset is quick—typically 1 to 2 hours after exposure—triggers are easier to identify and avoid in the future. |
Causes of Hives
The reason for hives rashes is that mast cells and basophils on the skin get stimulated and release histamine, causing local blood vessels to expand and form itchy welts.
Acute hives are triggered by external stimuli like drug allergies (common ones include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or Aspirin ), food allergies (such as shellfish, chocolate, or nuts), animal allergies, insect bites, or infections.
Chronic hives are trickier to pin down to a single cause, stemming from immune system imbalances where the body produces “autoantibodies” that stimulate mast cells. Triggers for physical hives include temperature changes, sunlight, intense exercise, sweating, stress, emotions, hormonal shifts, or even pressing or scratching the skin, which releases histamine.
Plus, autoimmune diseases like lupus and thyroid issues can lead to antibodies targeting mast cells, releasing histamine; chronic infections or inflammations such as H. pylori gastritis, sinusitis , pneumonia, hepatitis , tooth decay or urinary tract infections , and even malignant tumors can raise the risk of hives. Recent studies also link gut microbiome dysbiosis closely to chronic hives , so sticking to a healthy balanced diet , regular exercise , and a consistent sleep routine can make a big difference in managing chronic hives .
Hives Symptoms
Hives symptoms are easy to spot. You’ll see slightly raised, red patches on the skin all over the body. These patches feel a bit firm, vary in size and shape, and are incredibly itchy.
When hives break out, if you scratch an unaffected area, similar red patches might appear around it. But these dense, widespread, and intensely itchy red patches can vanish suddenly within a few hours. However, some patients may develop angioedema, leading to severe symptoms like swollen eyes, lips, narrowed airways, and breathing difficulties.
Hives First Aid & Itch Relief
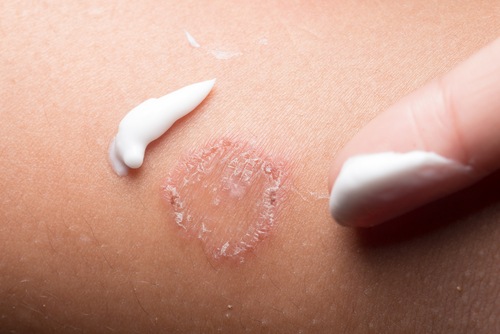
Ointment
When hives first appear, it’s recommended to apply an ointment with menthol or steroid ingredients to the red and itchy areas, or use a cold compress. The cooling sensation helps relieve itchiness and reduce swelling, but these methods are only supplementary and for short-term symptom control.
Allergy Medication: Antihistamines
Taking allergy medication like antihistamines is effective for preventing hives and treating chronic urticaria. Antihistamines neutralize the histamine released by stimulated mast cells in the skin, thus alleviating allergic symptoms.
Biologics
In recent years, targeted biologics for chronic hives treatment have emerged, directly addressing the culprits that stimulate mast cells. Anti-immunoglobulin E (anti-IgE) is suitable for patients whose symptoms don’t improve even with high-dose antihistamines.
Hives is closely linked to an imbalanced immune system. Besides autoantibodies stimulating mast cells, autoimmune diseases like lupus and thyroid issues can also be connected to hives.
For hives, you can take oral anti-allergy medications like antihistamines and biologics. Since hives originate from histamine in the dermis, the most effective treatment is antihistamine drugs. Anti-immunoglobulin E (anti-IgE) is suitable for patients whose symptoms don’t ease even with high-dose antihistamines.
Most cases of hives are not hereditary. However, chronic hives can stem from autoimmune diseases like lupus and thyroid issues, which may have a genetic component.
Hives is a common skin condition caused by an imbalanced immune system and is not contagious.
For chronic hives patients with stable conditions, the risk of vaccination is very low. A small number of people may experience acute hives as an allergic reaction to the vaccine, but early treatment usually prevents serious issues. If in doubt, consult your family doctor.
About the Author
Dr. Steven Loo
- Dermatology and Venereology
- Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery, The Chinese University of Hong Kong
- Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians (UK)
- Fellow of the Hong Kong College of Physicians
- Fellow of the Hong Kong Academy of Medicine (Medicine)
- Master of Science in Endocrinology and Diabetes, The Chinese University of Hong Kong
- Master of Science in Genomics and Bioinformatics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong
- Honorary Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh
- Honorary Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Glasgow